CubeFS in NetEase game business practice
Business introduction-elk-saas
Elasticsearch's hosting platform is the elasticsearch saas platform of NetEase Games' internal benchmark against external cloud providers. It can quickly create, easily manage, expand and shrink ES clusters, and simplify complex operation and maintenance operations.
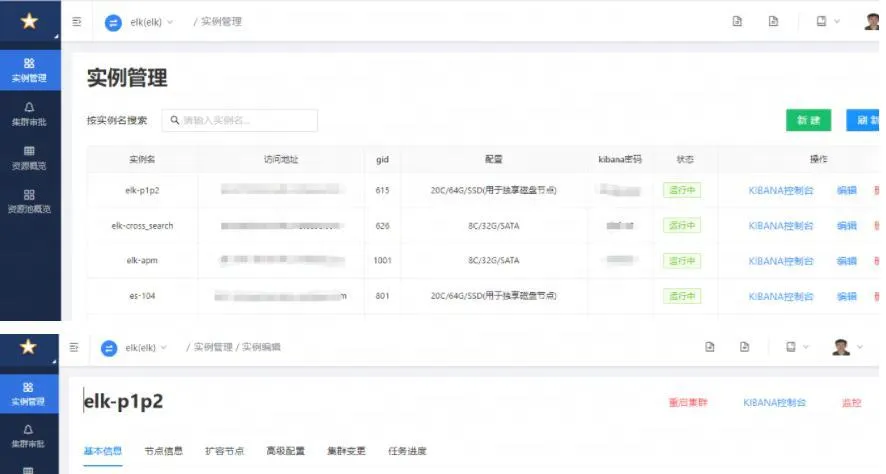
ES deployment architecture
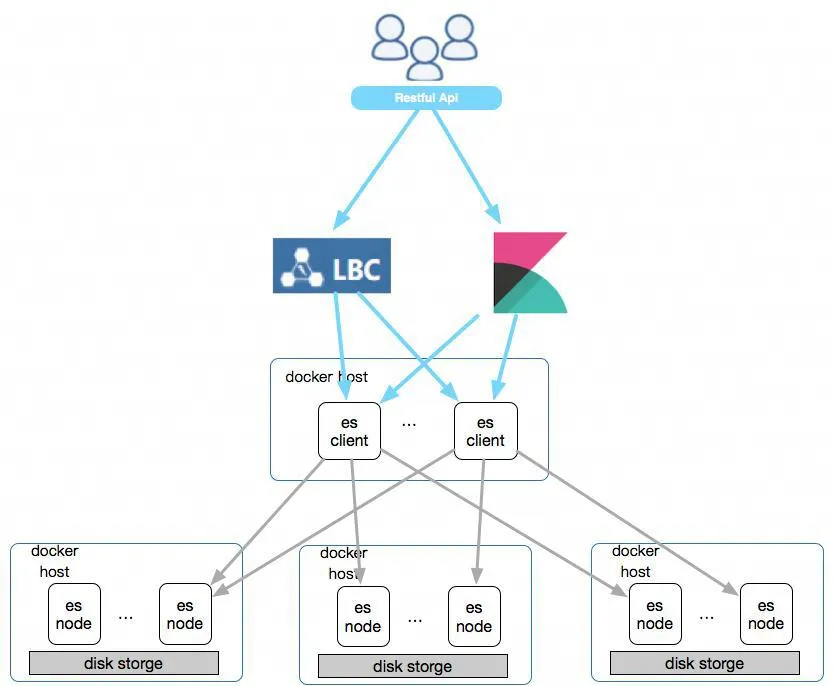
A cluster is created and spread out on different hosts. The hosts mix nodes of multiple ES clusters. Users access the ES cluster through a LoaldBalance service, which provides whitelist restrictions and limits CPU memory through Docker. Disk storage does RAID 10 for local disks and limits the disk space that can be used through LVM.
Operational pain points before accessing CubeFS
Different business clusters have different requirements for disk and CPU/memory ratios. There may be situations where disks or CPU/memory are idle and cannot be allocated. The new ES scheduling calculation allocation rate is low. Resources are severely fragmented.
On some hosts, disk IO is exploded, and non-self-maintained ES cluster write traffic cannot be scheduled. The corresponding ES node can only be offline. The offline process is long and dangerous (the same is true for bad machines, ES defaults to a single copy), and the same Some host disks are also allocated, but the IO is almost 0 and becomes a silent cost.
With the iteration of hardware, disks with different capacities have intensified the first pain point, and as the scale grows, more and more waste occurs.
Separating computing and storage seems to solve most problems? At this time, cubefs practice entered our field of vision and solved most of the problems we encountered better.
business practices
planning
ES and storage media types
Log-type ES uses hot and cold separation. The hot node is deployed exclusively with physical SSD. The stale node is deployed with a cfs volume. One ES node uses one cfs volume. After entering the stale node, we remove the ES copy. Data reliability is provided by CFS. Three copies to ensure
Business ES has higher CPU requirements than disk requirements. It provides
Cloud storage SATA
Cloud storage SSD
Physical SSD Higher SLA and performance
SSD multi-CFS cluster
Users do not have high requirements for SSD capacity, so the scale of the CFS cluster is not large. We created dual CFS clusters (actually it can also be divided by CFS ZONE), so that one ES cluster node volume can be created on two SSD CFS clusters respectively, which reduces the cost of ES. The risk of the cluster becoming completely unavailable.
capacity planning
Regularly create a new volume and run a benchmark test before deleting the volume. If there is no obvious change, it is considered normal. Basically, no problems have been encountered. You only need to monitor the meta and data related usage ratio radio, and expand the capacity regularly.
Access and maintenance
Create ES node
The user applies for a cluster or expansion, and the platform layer application determines whether the CFS has sufficient capacity. The precondition is that anti-affinity does not allow the same cluster to be deployed on the same host, and the machine with the highest matching score is selected based on the instance specifications.
Create a volume. For the host to mount the corresponding volume, the docker container mounts the data directory through -v.
The host can be a pure blade service, or it can be mixed on the CFS DN server.
Migrate ES nodes
When a machine fails or resources need to be scheduled, simply mount the volume to the new host, deploy it once with the original parameters and call back the platform API to update the data.
detail
Turning off followread will cause problems in extreme cases. ES has higher requirements for file consistency.
Turning off writecache and turning on writecache improves performance, but the IO interruption caused by flushing dirty pages is unacceptable. The local disk does not have this problem.
Volume indicator monitoring uses pushgateway to actively push to the monitoring server instead of pulling.
Log-type ES is configured with a more passive balancing strategy. The frequency of hot and cold migration is changed from once in the morning to once every hour to smooth disk IO consumption as much as possible.
scale and revenue
Carrying several PB + data, hundreds + ES nodes, hundreds + ES clusters
Reduced operation and maintenance complexity
ES has the ability to drift. If the host fails, maintenance and resource allocation can be quickly restored without waiting for ES to balance and restore data.
The CFS bad disk replacement process is unified and does not focus on specific business and host IO consumption as before.
The resource utilization rate is improved, and the actual usage is counted, providing almost unlimited expansion space. We have measured and compared the LVM host group that has been allocated by ES in the early stage (the CPU is actually only 60% sold, and the disk is only sold). 39%), if the same hardware configuration is redeployed with CFS and including CFS 3 copies, it is only 43% of the original solution.
disk:
90% of the CFS node disks are used. This is a goal that was completely impossible for physical disks to reach. Inconsistencies in disk capacity caused by physical disk upgrades do not need to be paid attention to anymore.
Disks no longer need to be used in Raid 10 to reduce machine failure rate
- Computing resources: Each host can be completely allocated. If DN computing resources are insufficient, use blades or 1U servers to supplement them.
Business Introduction-ES Searchable Snapshot
ES historical index backup can be packaged into snapshots to the remote end (which can be shared storage or s3). The data in the snapshot can be searched in real time through the self-developed plug-in, and some small files can be cached to the local disk after the search to speed up the next time. Search, suitable for low-frequency query scenarios of historical cold data, is a function of ES under elk-saas. Method 1: Mount using the mount command
As the cubefs community launched erasure coding, we tested the machine and put it online. Compared with 3 copies, it only needs to store 1.5 copies to ensure high data availability and bring higher redundancy than 3 copies.
Performance Testing
The file read and write benchmark latency is about 3-4 times slower than the three replicas. In other words, if the business scenario is that the more small files there are, the greater the gap between the three copies may be.
Our business is ES searchable snapshots. You can search the index in the snapshot in real time through self-developed searchable snapshots. Without local cache, erasure coding will be about 30% slower than three copies. If there is a local cache, there will be no difference.
Access and maintenance
We mount the same CFS volume to each ES node in the same cluster through cfs-client. A problem with cfs-client here is that the memory usage is too high. We need to remount and restart ES regularly to release the memory usage and wait for the community. repair
We hope to access through the s3 interface, but unfortunately there are still several bug fixes that require community integration and are currently unavailable. Compared with cfs-client fuse access, s3 access is less intrusive to the business and more maintainable.
Erasure coding component
From my personal understanding, you have to see the official website for a complete explanation.
The access node is responsible for data upload, download and real-time encoding, so it requires a machine with better CPU
blobnode is responsible for actually storing data
clustermgr is responsible for allocating writable volumes
The schedule is responsible for deleting and repairing data, and relies on kafka topics to record information. Note that the topic retention time must be written longer, otherwise the consumption topic may not be able to keep up and be cleared due to some reasons.
MetaNode, the erasure coding subsystem can upload and download through the interface, but it needs to record its own metadata, that is, where it exists and where it is downloaded from. MetaNode is reused here; additional writes are not currently supported.
detail
Choose the encoding mode reasonably. If the number of nodes is not large, choose the encoding mode with small slices as much as possible. For example, 10+4 means cutting the data into 10 parts, and 4 parts are check codes.
Host aware must be turned on online, so as to achieve true high availability and avoid load imbalance in later expansion. Assuming 10+4 encoding, at least 14 servers are required.
Set a reasonable timeout to avoid too many connections.
The XFS file system will pre-allocate space, resulting in inconsistency with the actual used space. The EXT4 file system does not have this problem.
If you change one parameter and leave the others unchanged, you may be able to pull it up, but you will encounter pitfalls later. For example, clustermgr's chunk_size and code_mode_policies are related to each other and are also related to blobnode's max_chunk.
scale and revenue
The currently used capacity is several PB (actually 1.5 copies are stored). Under 10 Gbps download bandwidth, the download delay is no higher than 5ms.
The three-replica node has been scaled down, and erasure coding only requires half the original cost.
Data redundancy is lower than three copies, but data durability is higher
Follow-up plan
s3 can be used
QOS speed limit can be used. We don’t need such a fast speed for uploading, because too fast will also put IO pressure on the backup end.
Business Introduction-Machine Learning Business
Tmax one-stop machine learning platform covers the entire process of machine learning engineering development [data management -> algorithm research and development -> model training -> service stress testing -> deployment -> A/B testing -> online -> online maintenance]
Early data volume storage used nfs + local disk SSD and other distributed storage, k8s scheduling + corresponding csi plug-in
Operational pain points before accessing CubeFS
The NFS client is unstable, with good single-machine performance and poor scalability. Multiple single-machine loads are unbalanced and easily exploded. There is no task-level IO monitoring.
Other distributed storage solutions are mature, but their small file performance is poor and unstable, and the heap hardware is not cost-effective.
Other distributed storage B relies heavily on client cache and has poor performance after cache misses. It is essentially a supplement to solution A. After thorough testing and backed by large-scale practical experience with ES, the data volume uses CFS volumes combined with K8S.
Access plan
Why is the k8s csi protocol not used?
Container Storage Interface (CSI), referred to as CSI, CSI attempts to establish an industry standard interface specification. With the help of the CSI container orchestration system (CO), any storage system can be exposed to its own container workload.
The configuration items of cfs-client are not fully supported. Some are because the csi interface definition itself does not exist, and some are because the plug-in code does not support it and the plug-in code needs to be modified.
When csi is updated or restarted abnormally, all underground clients will be killed, causing business to be affected. This is a common problem with csi fuse-related plug-ins. K8s has opened many issues to discuss https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/issues/70013
The final proposal
Adopt k8s init container + write app server + k8s host path solution
The main container will be started only after all Init Containers have been executed.
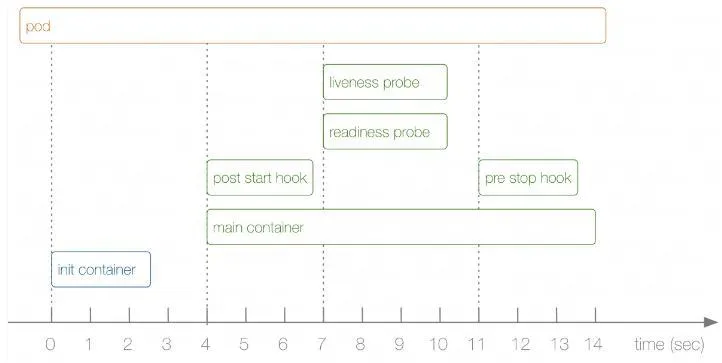
The pod calls the init Container shared host Socket to mount the volume to the host.
Share to business containers through host path
The business container will not start until the mounting is successful.
can be realised
Training task granularity IO monitoring and restriction
Full support for cfs-client configuration items
It will not be like csi when the plug-in hangs and all cfs-clients are killed.
File directories can be managed through the s3 gateway.
detail
followread is enabled
Network latency is very important. The client and server should not switch across cores. The latency should be less than 0.8ms.
The memory consumption of metanode is many times greater than that of es business. For capacity estimation, please refer to the official website documentation.
Scale and revenue
Hosts PB+ data, hundreds of volumes
The training speed has been greatly improved, far better than NFS, and the read IOPS can reach hundreds of K
Hardware costs are lower than other options
Hosts hundreds of millions of small files and runs stably
Business Introduction-Hybrid Cloud Acceleration
Due to the uncertainty of the business, the high cost of purchasing graphics cards and the timeliness of delivery, we will purchase cloud graphics cards from cloud vendors for use. Due to the confidentiality of the data content, there is no need to store a complete data with the cloud vendor, so the network Latency will become a big problem, and reading data too slowly will cause the graphics card to become unloaded, resulting in a waste of time and money.
It just so happens that cfs has a cfs-bcache component, which can cache qualified data to the local disk after reading it once.
Therefore, we preheat commonly used data and then package snapshots. The newly opened machines come with part of the cache to avoid frequent cache pulls that waste bandwidth and time.
The biggest benefit is that it makes it possible to rent a cloud provider's graphics card to become a hybrid cloud.
about the author
Rui Zhang, one of the CubeFS Contributors, is responsible for elasticsearch related work and currently works at NetEase Games.